
Dots 1, 2 and 3 are found on the left.
Dots 4, 5 and 6 are on the right.
Each dot forms into something-wheatear it's a letter, number, symbol, punctuation mark or part of a contraction.
About Louis Braille Louis Braille (1809-1852) designed a coding system, based on patterns of raised dots, which the blind could read by touch. Born in Coupvray, France, Braille was accidentally blinded in one eye at the age of three. Within two years, a disease in his other eye left him completely blind.
In 1819, Braille received a scholarship to the Institut National des Jeunes Aveugles (National Institute of Blind Youth), founded by Valentin HaŁy (1745-1822). The same year Braille entered the school, Captain Charles Barbier invented sonography, or nightwriting, a system of embossed symbols used by soldiers to communicate silently at night on the battlefield. Inspired by a lecture Barbier gave at the Institute a few years later, the fifteen-year-old Braille adapted Barbier's system to replace HaŁy's awkward embossed type, which he and his classmates had been obliged to learn.
In his initial study, Braille had experimented with geometric shapes cut from leather as well as with nails and tacks hammered into boards. He finally settled on a fingertip-sized six-dot code, based on the twenty-five letters of the alphabet, which could be recognized with a single contact of one digit. By varying the number and placement of dots, he coded letters, punctuation, numbers, diphthongs, familiar words, scientific symbols, mathematical and musical notation, and capitalization. With the right hand, the reader touched individual dots and, with the left, moved on toward the next line, comprehending as smoothly and rapidly as sighted readers. Using the Braille system, students were also able to take notes and write themes by punching dots into paper with a pointed stylus which was aligned with a metal guide.
At the age of twenty, Braille published a monograph describing the use of his coded system. In 1837, he issued a second publication featuring an expanded system of coding text. Despite the students' favorable response to the Braille code, sighted instructors and school board members, fearing for their jobs should the number of well-educated blind individuals increase, opposed his system.
Braille grew seriously ill with incurable tuberculosis in 1835 and was forced to resign his teaching post. The Braille writing system - though demonstrated at the Paris Exposition of Industry in 1834 and praised by King Louis-Philippe - was not fully accepted until 1854, two years after the inventor's death. The system underwent periodic alteration; the standardized system employed today was first used in the United States in 1860 at the Missouri School for the Blind.
The Braille Cell
 | Braille is formed by a cell of 6 dots: Dots 1, 2 and 3 are found on the left. Dots 4, 5 and 6 are on the right. Each dot forms into something-wheatear it's a letter, number, symbol, punctuation mark or part of a contraction. |
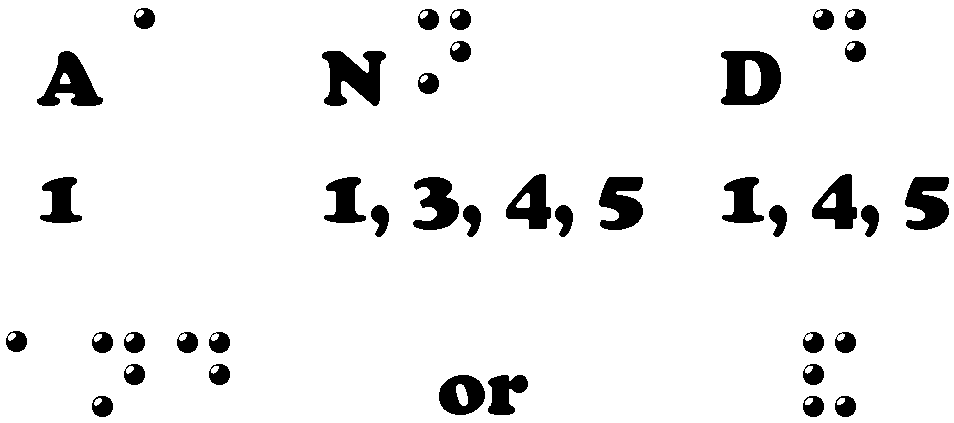
3 Grades to BrailleBraille has 3 levels (or grades) to go by. Each grade has its own uniqueness.
Grade 1 Braille
All 26 letters of the alphabet.
Numbers 1 - 0 (letters A - J with number sign in front.)
Punctuation marks
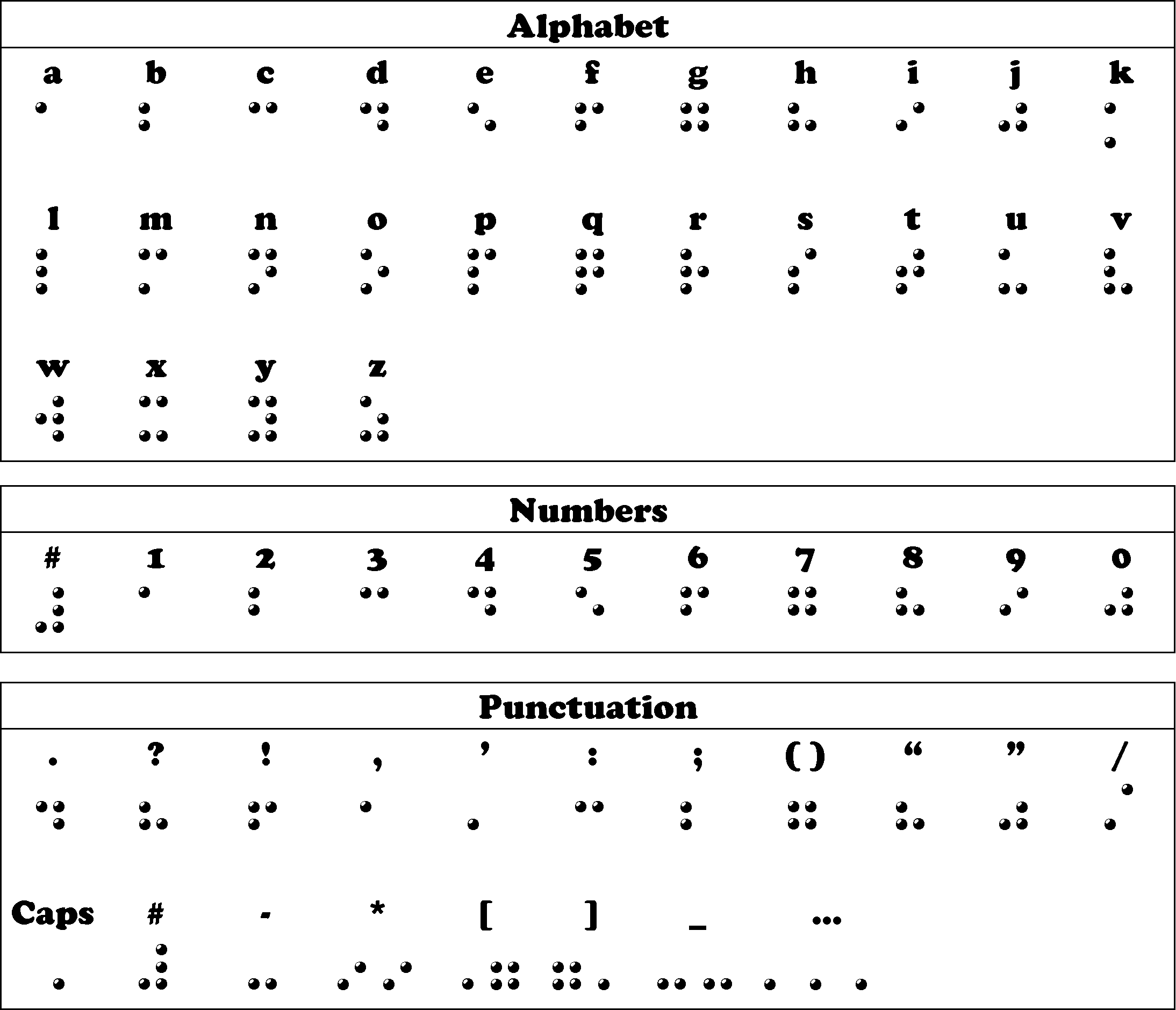
Image: Alphabet, Numbers & Punctuation
Grade 2 Braille
Contractions make up grade 2 braille. 189 words in this catagory can be used to shorten a word thus shortening a sentence. This allows for faster and easy reading. Not all words can be contracted, and there are strict rules for using them.
Images: Examples of the word Braille in Grade 1 & 2 Braille: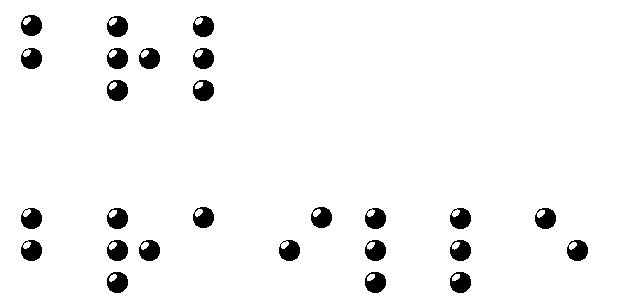
Image: Contractions List
Grade 3 Braille
mathematics
music
chemistry
advanced contractions
No images for grade 3 braille are provided.
Usage & Tools of Braille Uses